ILA Port Strike: Rising Congestion and Economic Impact
English - Ngày đăng : 18:05, 04/10/2024

Severe Port Congestion and Prolonged Risk
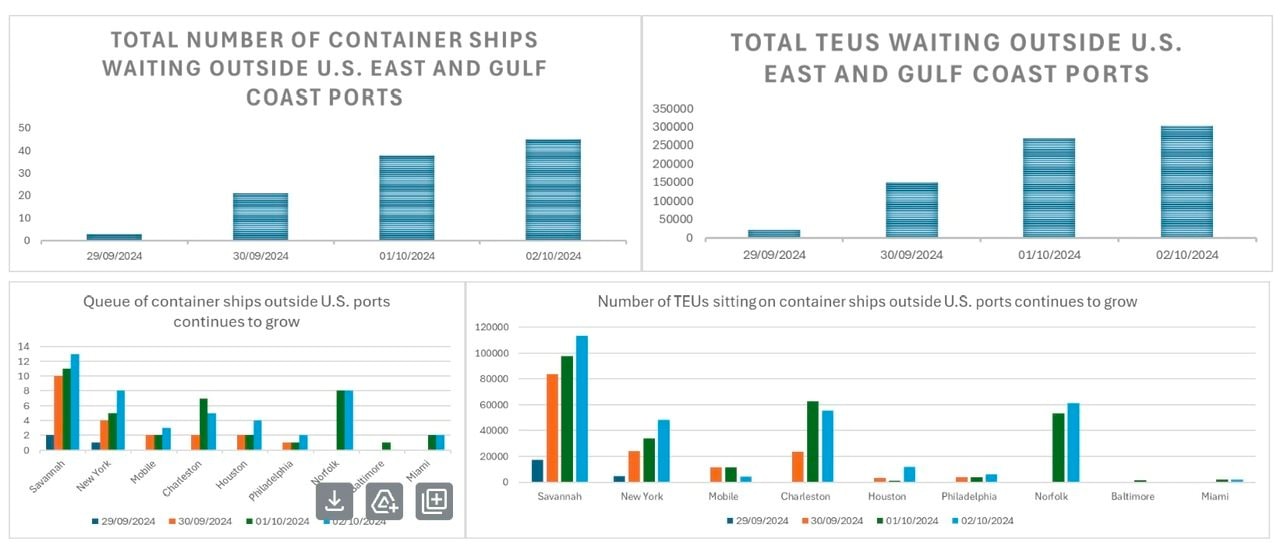
According to Everstream Analytics, as of October 2, over 45 container vessels are anchored near major U.S. ports, a sharp increase from just three ships on September 29. These ships have a combined cargo capacity exceeding 300,000 TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units). The vessels are primarily concentrated outside key ports, including Savannah (13 vessels), New York (8 vessels), and Norfolk (8 vessels).
While shipping companies hope for a quick resolution to the strike, there have been no signs of diverting vessels to ports in the Bahamas, Mexico, or the U.S. West Coast. If the strike continues without an agreement, vessel diversions will likely become inevitable.
Joseph Firrincieli, Sales Manager at OEC Group New York, warns that "one week of a strike will result in approximately one month of congestion, backlogs, and delays." This means that consumers could face empty store shelves and rising prices in the coming weeks".
Economic Impact and Supply Chain Disruptions
It is estimated that the strike could cost the U.S. economy up to $5 billion per day. This is particularly concerning given that 60% of U.S. imports and 10% of global container trade pass through these ports.
Imports from Europe, Central America, and South America will be heavily impacted, especially perishable goods. Data shows that 78% of dates, figs, and pineapples; 75% of bananas; and 81% of plywood and stone materials are imported through East and Gulf Coast ports. For perishable items such as agricultural products and pharmaceuticals, disruptions could occur within 1-2 weeks, while general consumer goods may face delays in 3-4 weeks.
Furthermore, container shipping rates are on the rise. When the strike was announced, the International Longshoremen's Association (ILA) reported that ocean carriers were charging up to $30,000 per container, a dramatic increase from $6,000 just weeks prior. However, data from Xeneta, a freight rate analytics platform, suggests actual rates are much lower, with average spot rates around $7,000 for containers from the Far East to the U.S. East Coast.
The ILA dockworker strike is causing severe consequences for U.S. supply chains and the broader economy. While the short-term impacts are clear, businesses and consumers must brace for further challenges in the near future. From port congestion and shipment delays to rising consumer prices, this situation demands timely responses from all involved parties.
Although certain sectors of the U.S. economy, such as domestic production and trade with Canada and Mexico, remain stable, the import and retail industries are feeling the strain. Swift negotiations between dockworkers and port managers are essential to mitigate economic fallout and stabilize supply chains. In the meantime, businesses should closely monitor the situation and explore alternative solutions, such as using other ports or adjusting supply chains to minimize risks.
Ultimately, the sustainability of supply chains heavily depends on the collaboration between businesses and governments to address the strike and future disruptions. It is crucial to assess the economic impact thoroughly and ensure that global supply chains can withstand similar shocks in the future.
